- It is a measure used to describe the sharpness and clarity of an image or picture.
- Resolution is especially popular in the mobile industry for describing a mobile device's display capabilities, and also in the entertainment media to distinguish the visual quality of movies.
- Pixel resolution:
- It is the number of pixels contained on a display monitor, expressed in terms of the number of pixels on the horizontal axis and the number on the vertical axis.
- The same pixel resolution will be sharper on a smaller monitor and gradually lose sharpness on larger monitors because the same number of pixels are being spread out over a larger number of inches.
- For example , an image that is 2048 pixels in width and 1536 pixels in height has a total of 2048×1536 = 3,145,728 pixels or 3.1 megapixels.
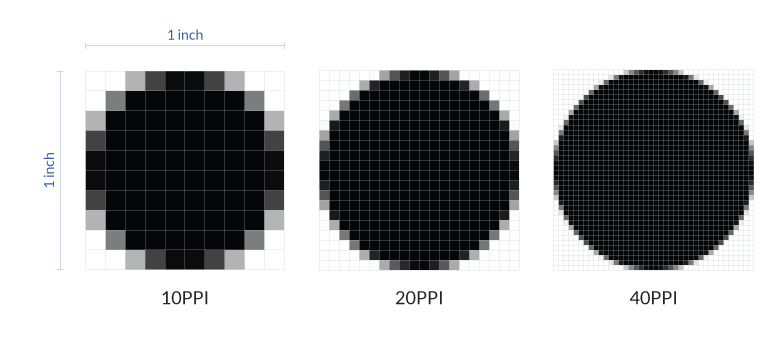

- Spatial Resolution:
- It states that the clarity of an image cannot be determined by the pixel resolution. The number of pixels in an image does not matter.
- Spatial resolution can be defined as the smallest visible detail in an image.
- It refers to that we cannot compare two different types of images to see that which one is clear or which one is not.
- For example:
- We cannot compare these two images to see the clarity of the image.


- The picture on the top is zoomed out picture of Einstein with dimensions of 227 x 222. Whereas the picture on the bottom has the dimensions of 980 X 749 and also it is a zoomed image.
- We cannot compare them to see that which one is more clear. Remember the factor of zoom does not matter in this condition, the only thing that matters is that these two pictures are not equal.


- Both the pictures has same dimensions which are of 227 X 222.
- Now when we compare them, we will see that the picture on the top has more spatial resolution or it is more clear then the picture on the bottom. That is because the picture on the right is a blurred image.
- Spectral resolution:
- Spectral resolution is the ability to resolve spectral features and bands into their separate components.
- Multispectral Images can resolve even finer differences of spectrum by measuring and storing more than the traditional 3 of common RGB color images.

- Radiometric resolution:

- Radiometric resolution determines how finely a system can represent or distinguish differences of intensity, and is usually expressed as a number of levels or a number of bits.
- The higher the radiometric resolution, the better subtle differences of intensity can be represented.



